A SQL Governor installation consists of the SQL Governor server itself and any number of proxy services. The SQL Governor server acts as a central repository and stores all of the data collected by the proxies. At a minimum, one proxy per domain is required, but more proxies can be installed to balance the load (the proxy itself uses a minimal footprint of 1-2% CPU on the server, however). One proxy supports collecting data from up to 25 servers.
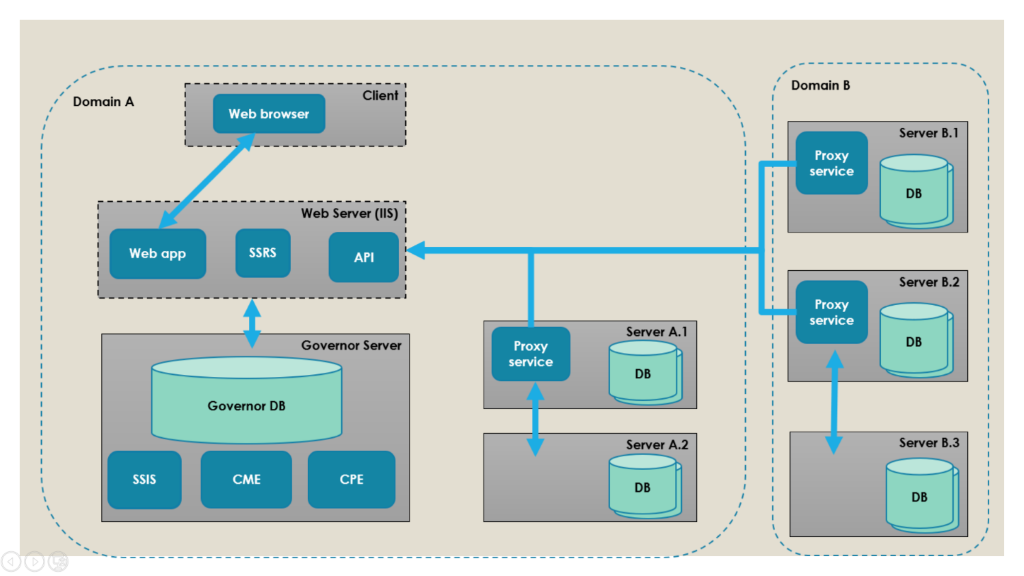
The graph above shows one possible configuration of the architecture. In this example, the SQL Governor database and the SSIS catalog reside on the same server and the SQL Governor UI, SSRS and the Web API on another. Three proxies are installed: one collects data from servers A.1 and A.2 (both in domain A), one collects data from server B.1 and one from servers B.2 and B.3 (all under domain B). Note that the third proxy service is optional: one proxy installed on any of the servers in domain B would be enough to collect data from all three domain B servers. Separating the web server and the SQL Governor server is also optional, as they can both reside on the same server.